Teachers are passionate about ensuring their students move forward academically. And that’s exactly why relying on evidence-based practices and strategies is so important. With limited instructional time, employing effective approaches to instruction, including practices and strategies, helps educators support the needs of all their learners.
In this article, we’ll walk you through a sampling of several of the built-in, evidence-based practices and strategies in Unique Learning System that help educators boost student growth. Practices refer to content in curriculum or materials, and strategies refer to the approaches teachers use to deliver the instruction to students.
Practices & Strategies
Practices
Strategies
Practices
Systematic Instruction
The practice of systematic instruction includes having a carefully and purposely planned sequence of instruction to optimize performance for all students. An example of systematic instruction is offering instructional sessions with one or more trials to teach a desired skill, which drives student growth.
Example
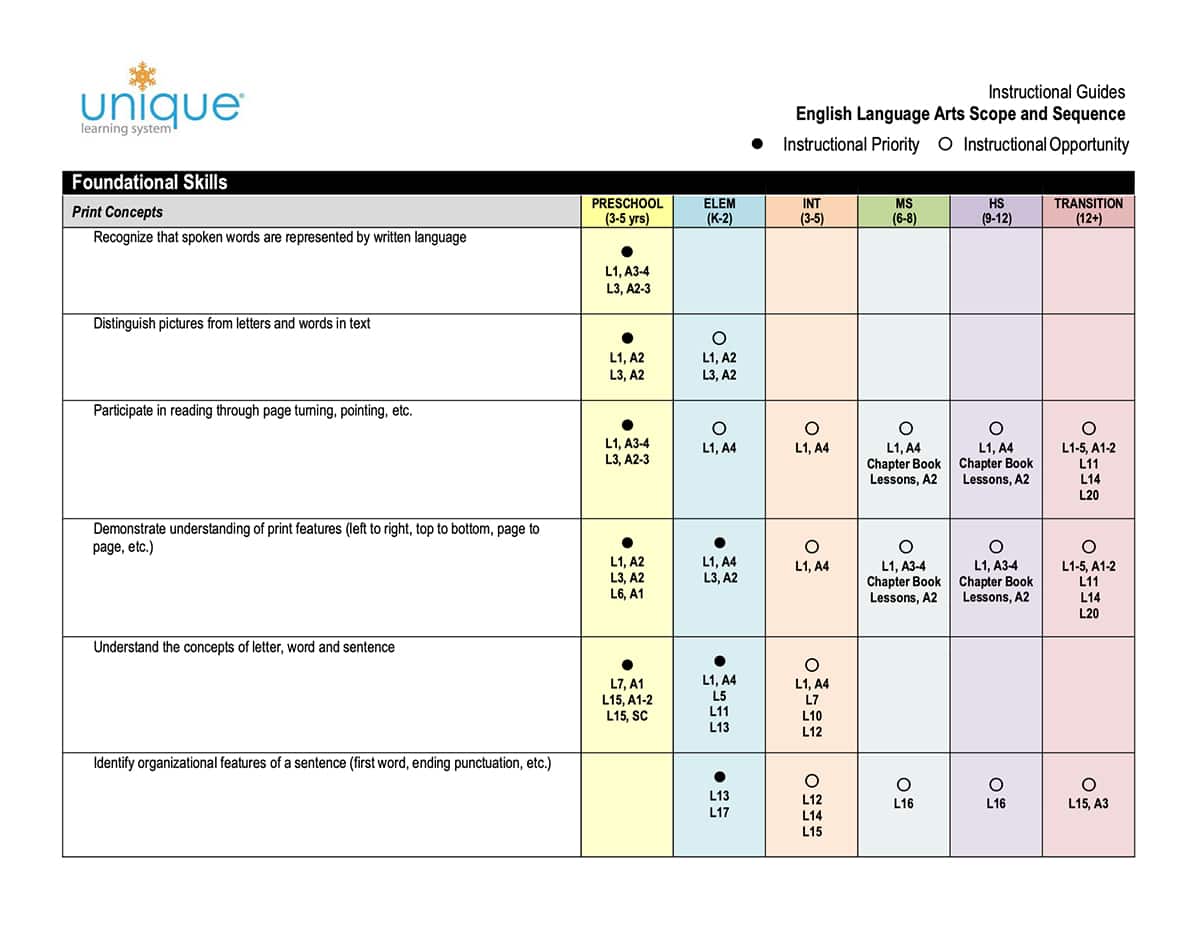
Educators can meet the needs of students with research-based methodologies in Unique Learning System. Lesson plans are based on a spiraling scope and sequence to best equip teachers to introduce a concept or skill, reinforce it, and support students in applying it. Unique Learning System provides instruction that enables students to apply skills across contexts to make meaningful connections with related skills.
Explicit Instruction
Teaching that is done in a direct, structured way with clear instructions is referred to as explicit instruction. One of the benefits of this type of instruction is that students know how to succeed from the beginning, and they are provided with ongoing feedback and many chances to practice what they’re learning. Plus, routines are established for teachers to provide explicit instruction.
Example

With Unique Learning System, educators establish student routines, build on consistency, and establish high expectations for learners. Routines are provided in standards-based lesson plans, and they give teachers explicit instruction, modeling, practice, review, and extension plans to follow Unique Learning System’s spiraling scope and sequence.
Interactive Read Aloud
When using the interactive read-aloud practice, teachers read aloud from a selected text, and pause occasionally for meaningful conversation. Educators engage in explicit instructional practices during the discussion, including modeling comprehension strategies, providing vocabulary instruction, scaffolding skills for comprehension, and giving corrective feedback.
Example
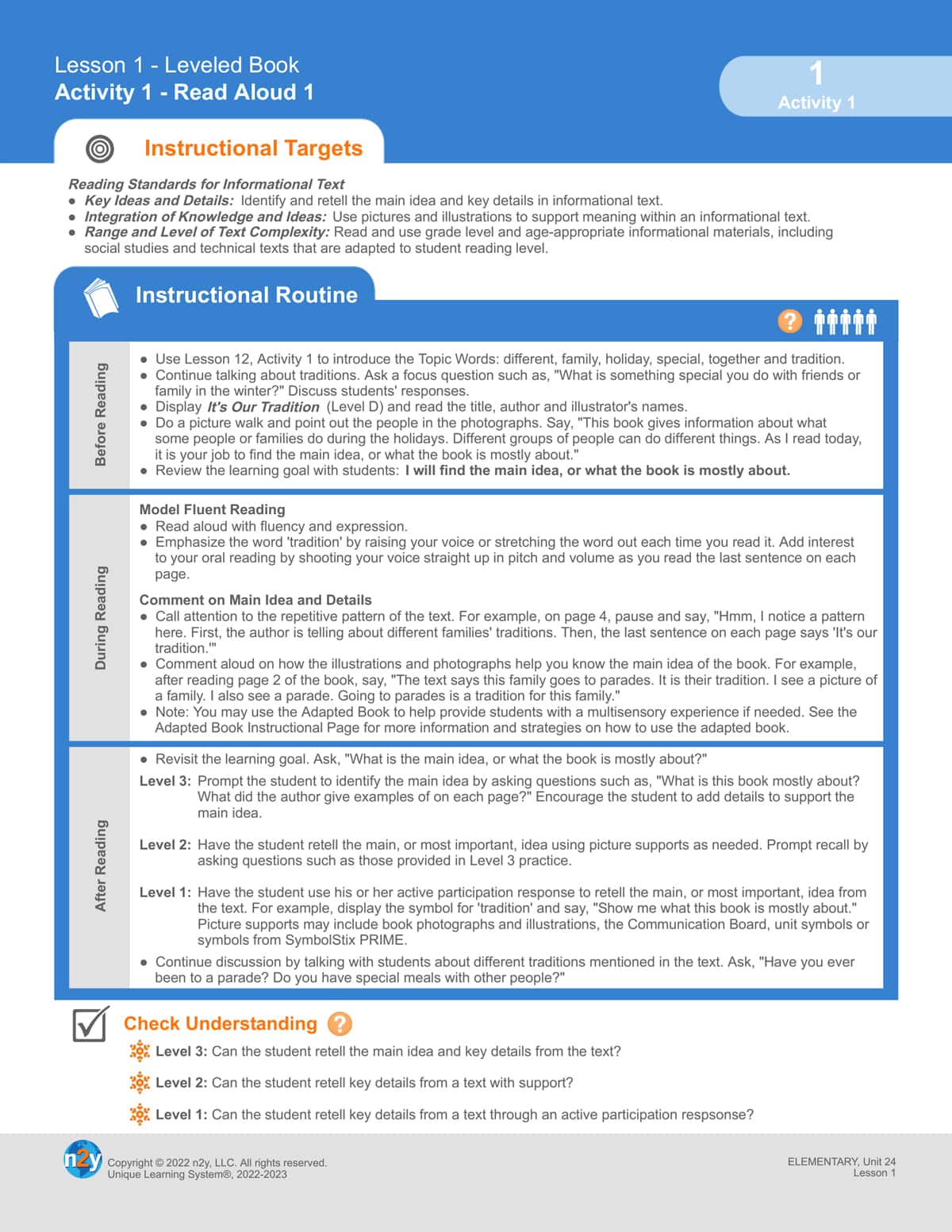
Unique Learning System’s instructional routines for read alouds save educators time since they use explicit, pre-made routines and questions. These routines provide practices for teachers to use before, during, and after the read aloud to activate prior knowledge, promote comprehension with scaffolded questioning, discuss vocabulary, and promote student choice. Learner engagement is improved, which helps students build stronger connections with the book, the world, and their personal lives.
Ask Questions
Asking questions is an evidence-based practice that allows teachers to check for understanding, stimulate recall, activate prior knowledge, promote comprehension, and build critical thinking skills. And as learning progresses, students answer questions presented by the adult leading the learning. This improved engagement allows students to build stronger connections to learning and extended learning promotes generalization.
Example

Unique Learning System includes appropriate challenges for students of all abilities and backgrounds. In instructional routines, specific questions are included for teachers to activate students’ prior knowledge, promote comprehension, and build critical thinking. Plus, Unique Learning System’s active participation scripts give teachers examples of how to ask questions of unique learners while providing single choices, errorless choices, and correct response choices.
Opportunities for Practice
Providing students chances to practice what they’ve learned allows them to apply skills that are being taught as well as those that were previously learned. Giving ample opportunities to practice in different formats allows students of varying ability levels to demonstrate their knowledge and improves engagement.
Example
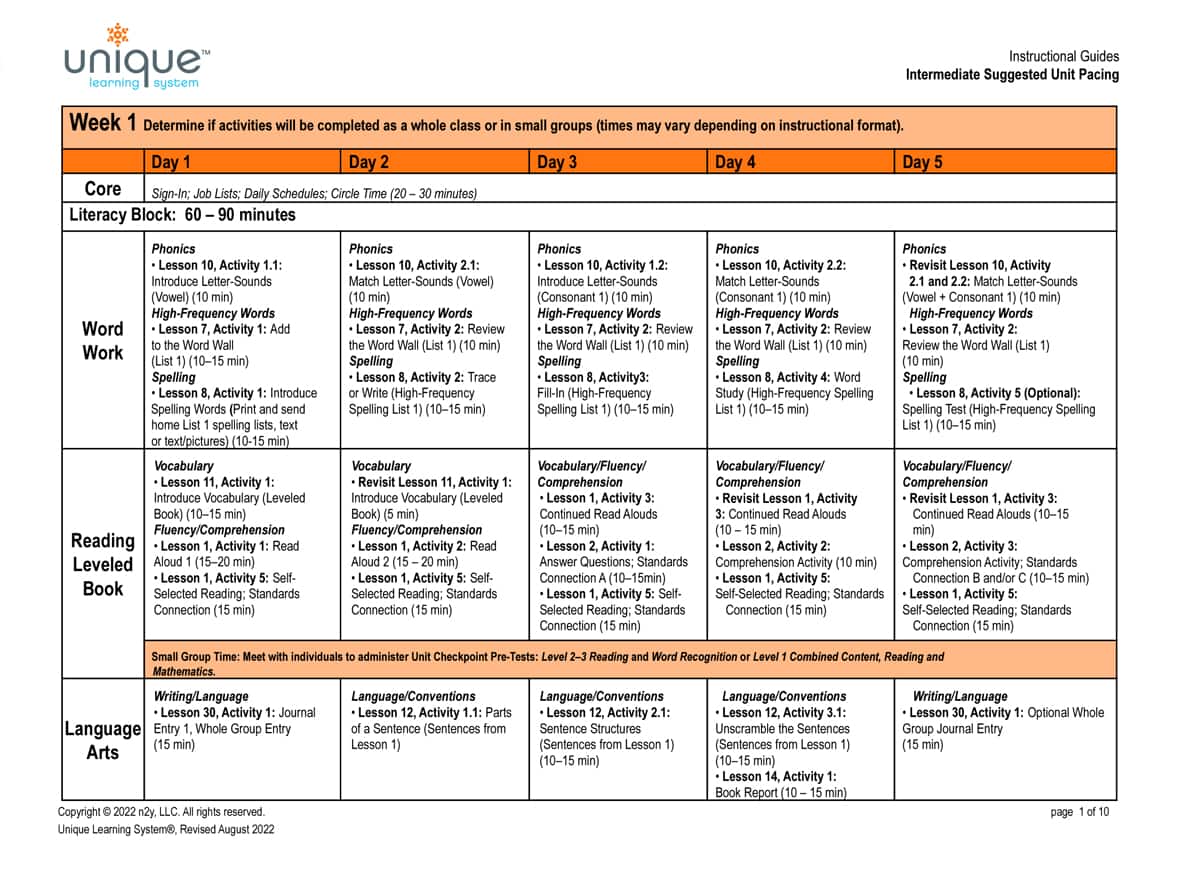
Unique Learning System’s suggested unit pacing provides four to five opportunities to practice a lesson or activity per month. In fact, the solution is based on an overall cross-unit structure that has students practice skills month over month and year over year using new situations to promote carryover and generalization. Having numerous chances to practice material allows students to build strong learning connections, promote generalization across subject areas, foster independence, and achieve meaningful outcomes.
Whole Group, Small Group, One‑on‑One
Students can practice in whole-group, small-group, or one‑on‑one settings. In a whole-group setting, educators can teach a topic or model a new concept to the entire class, or students can have a discussion as a whole class. When using small groups, students can work with each other or the teacher plus other students. And in one-on-one settings, students learn individually from a teacher. Individual settings can include interaction with the teacher providing specially designed instruction (SDI) to meet the specific learning and pacing needs of the student.
Example

Unique Learning System uses whole-, small-, and one-on-one grouping to introduce and practice skills. Plus, individual student needs are addressed with one-on-one instruction to practice skills, give assessments, and differentiate materials. Unique Learning System’s inclusive instruction means that many activities can be used in general education settings, too. Teachers save time with suggested groupings, empowering them to focus on helping learners achieve meaningful outcomes.
Strategies
Prompting
Prompting is a strategy that uses gesture, verbal, visual, or physical assistance to help a student learn a new skill or behavior or to direct a student to the correct answer.
Example

Teachers can deliver the right level of support to help all students with Unique Learning System. Lesson plans provide educators with specific prompt suggestions throughout instructional routines. Active participation scripts include prompting level suggestions with a goal of decreasing prompts over time. And the solution is easy to use right from the beginning, as built-in supports, such as visual prompts in assessments, remain consistent throughout.
Modeling
Modeling uses demonstration of a desired concept or behavior so learners can imitate it, which leads to acquiring the skill or behavior.
Example

Teachers save time with multiple areas of modeling support in Unique Learning System. Lesson plans include built-in, explicit modeling guides throughout each instructional routine. Modeling opportunities in routines are provided for reading, communication, writing, math conventions and reasoning, science, transition lessons, and more!
Fading Strategies
Fading strategies subtly reduce prompts over time, which prevents prompt dependency and promotes skill-building and independence.
Example

Educators can promote independence with faded strategies incorporated into Unique Learning System lesson plans. Supports are included for students in Level 1 through Level 3, and as learners become more independent, teachers can provide faded support and move students to a higher level. And Unique Learning System supports fading of auditory and visual cues in more than just lesson plans!
Scaffolding
When using a scaffolding strategy, teachers distill concepts into chunks to present learners with more digestible information. Supports can be added during each chunk to help students grasp new material.
Example

Lesson plans and activities in Unique Learning System are based on a spiraling scope and sequence. And with the sequence provided, scaffolding is built in, and concepts are broken into manageable chunks so students achieve meaningful outcomes.
Reinforcement
A key element to teaching and behavior change, reinforcement applies a consequence following a learner’s response or behavior. Reinforcement increases the likelihood that a student will use the same response or skills in the future, and is an effective way of encouraging desired behaviors.
Example

Reinforcement boosts engagement, increases desired behaviors, and improves student relationships with teachers and other adults. Throughout Unique Learning System’s active participation guidelines, reinforcement is discussed in multiple locations. Auditory and visual reinforcement is embedded throughout instructional routines, including before, during, and after activities.
Corrective Feedback
Teachers engage in corrective feedback when they provide students with the exact steps and feedback needed after a task is completed. Corrective feedback helps learners succeed when they try again. Accurate responses demonstrate student progress and growth.
Example

In Unique Learning System’s instructional routines, teachers are provided with phrasing and wording to use when students answer questions during practice and review. This allows students to see themselves learning, understand how to make corrections, and try again to succeed. Auditory and visual feedback is provided for right and wrong answers, and students attain meaningful outcomes as they encounter appropriate challenges with increased skill acquisition.
Self-Regulated Strategy Development
When using the six progressive stages of writing instruction, educators can provide learners with opportunities to build responsibility and confidence with self-regulated strategy development. This improves student engagement by building stronger writing connections and extends learning across content areas.
Example

Writing lesson plans in Unique Learning System follow the six progressive stages. This includes starting by activating background knowledge, discussing a pre‑writing strategy to be learned in a particular lesson, modeling a strategy to be used, memorizing the strategy through repeated exposure, providing independent practice, and supporting regulation through life skills and transition lessons that teach and give opportunities to practice self‑regulation. Specific units on conflict and transition activities focus on self‑care, attitude, and other life skills students need for lifelong success.
Concrete, Visual, Abstract (CVA)
Educators can choose the CVA strategy for teaching math to promote students’ deep and sustainable understanding of math problem-solving. CVA empowers teachers and paraprofessionals to learn and use different methodologies. Plus, when educators use the CVA strategy, they build students’ early and complex math thinking. Supporting stepwise procedures in CVA increases accuracy and conceptual understanding.
Example
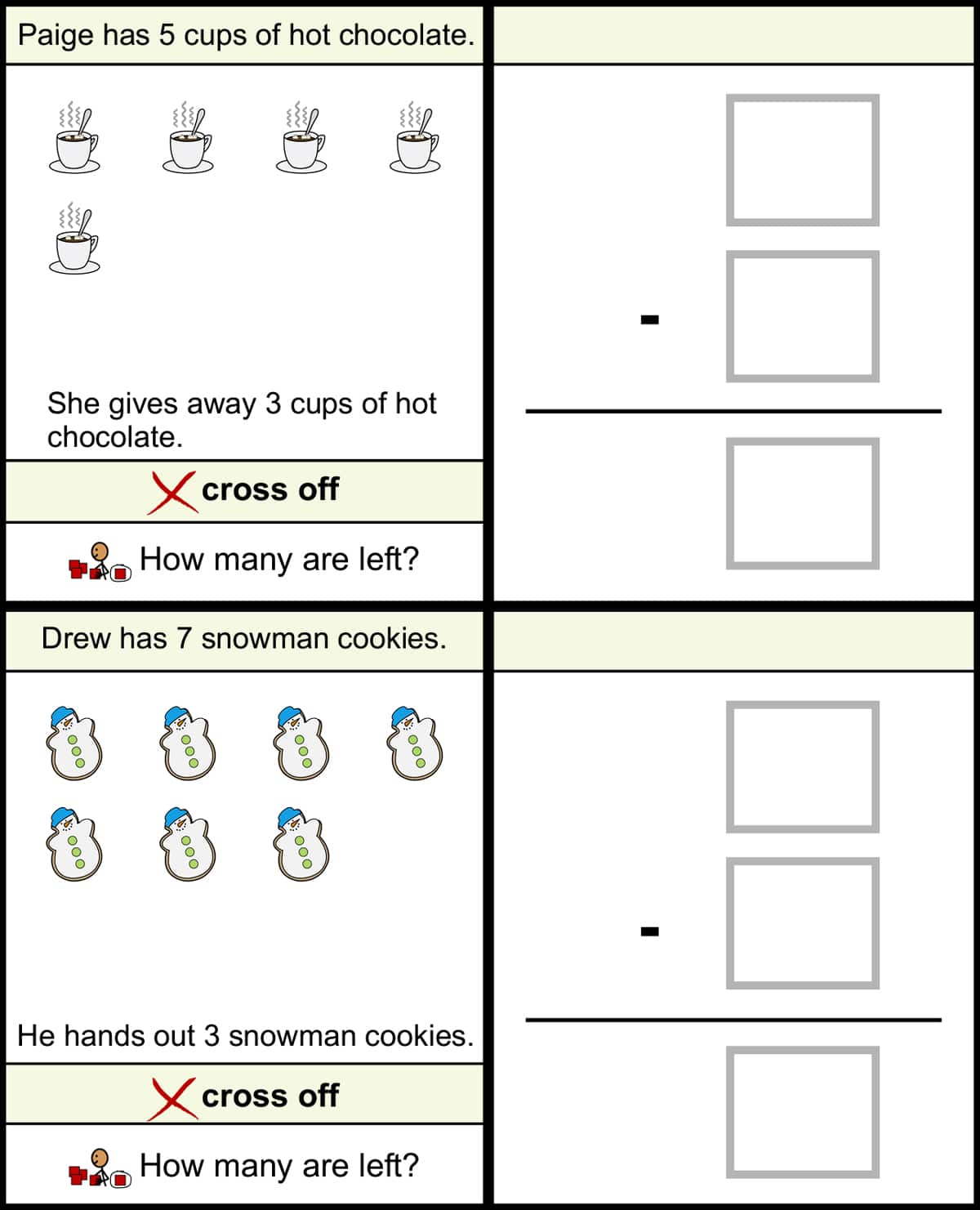
Unique Learning System lesson plans support the CVA sequence of math instruction. In differentiated Levels 1, 2, and 3, math lesson plans provide specific examples of when teachers should use concrete and visual strategies. Plus, Unique Learning System materials have built-in, scaffolded, concrete examples in math.
Clarify Expectations Before/After Instruction
Teachers can let students know exactly what behavior, work production, etc., is expected of them before instruction takes place and provide insight and feedback after instruction. Having consistent and clear expectations improves engagement and promotes student growth.
Example
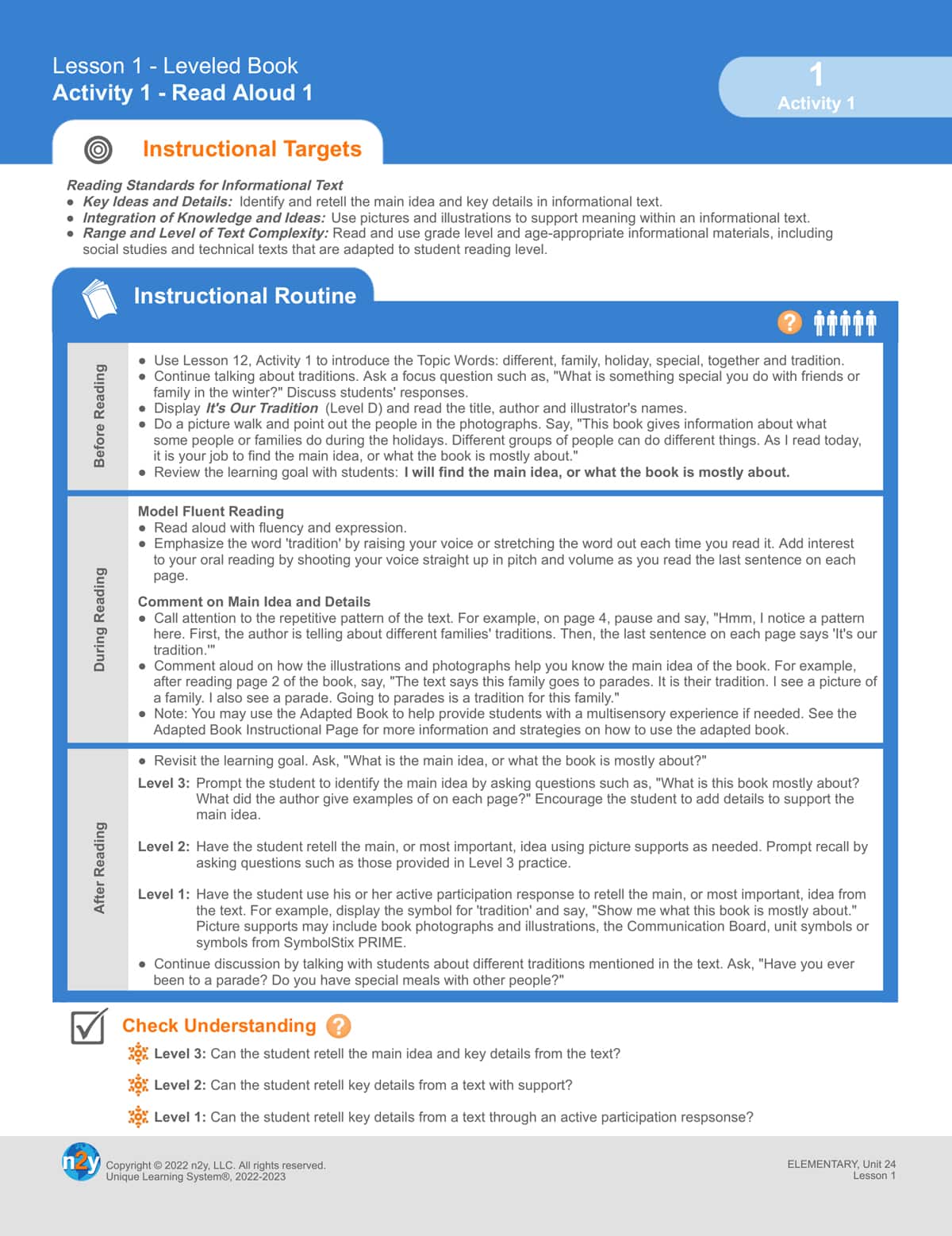
Unique Learning System’s instructional sequence provides learners with precisely what is expected before and after the explicit portion of each lesson. Students consistently have access to what is expected, which makes success more attainable. Plus, teachers save instructional time because learners know what to anticipate because of the consistency in Unique Learning System’s lessons!
Differentiation
Educators can meet each student’s specific and individualized needs by tailoring instruction, including the content, process, product, or environment. Personalized classroom instruction means students of varying abilities receive individualized challenges, which improves engagement and encourages independence.
Example

Unique Learning System lesson plans provide differentiated learning experiences for students at Level 3 through Level 1. Learners in Level 3 benefit from the greatest degree of independence, and those in Level 2 may require picture support and other supports. Students in Level 1 are participatory learners.
Structured Inquiry
Educators lead students in the structured inquiry strategy as they work through learning together. Teachers provide the lesson, materials, and detailed instruction; then, the class completes the inquiry together.
Example

With Unique Learning System, it’s easy for educators to provide structured inquiry so their class learns together, which promotes communication and team building. Lesson plans provide teachers with lessons, materials, and instructional routines. Educators are empowered with everything they need to provide structured inquiry!


